Lumens play a crucial role in outdoor and street lighting, serving as the primary measure of brightness. Selecting the right lumen count directly influences safety, aesthetics, and energy efficiency. Bright, well-lit areas deter potential threats, enhance visibility, and create a welcoming atmosphere. On the other hand, poorly lit spaces can compromise security and diminish the overall appeal of an area. Striking the right balance ensures not only a safer environment but also an energy-efficient solution that aligns with modern sustainability goals.
Many individuals and businesses face the challenge of choosing the appropriate brightness for their outdoor lighting needs. Some prioritize safety and visibility, while others focus on energy savings or aesthetic appeal. For instance, high-lumen lights, often used in large-scale projects like solar streetlights, can reach up to 40,000 lumens. However, for residential or small commercial applications, a range closer to 3,000 lumens often provides the perfect balance between brightness and practicality.
This article aims to guide you through the process of selecting the ideal lumens for various outdoor lighting applications. By understanding how lumens impact different aspects of lighting, you’ll be equipped to make informed decisions that enhance safety, improve energy efficiency, and elevate the visual appeal of your outdoor spaces.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are Lumens and Why Do They Matter?
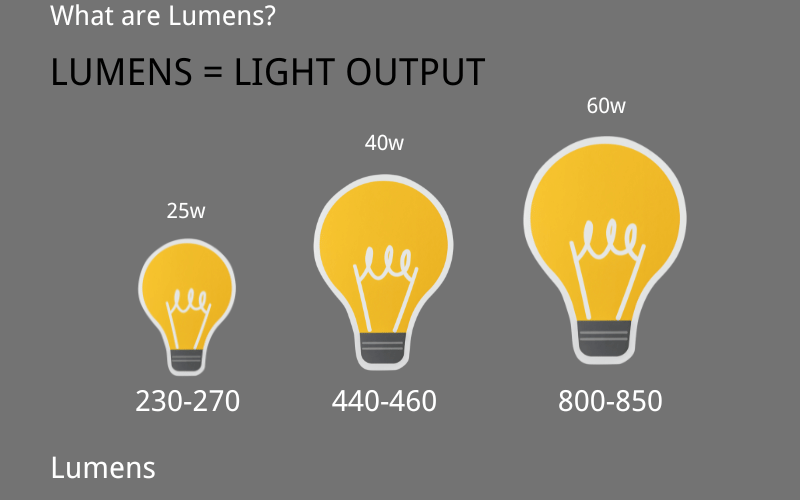
In my decades of working with solar street lighting, I’ve found that one of the most misunderstood terms in lighting is “lumens.” Simply put, lumens measure the total amount of visible light emitted by a source. Think of lumens as the true indicator of brightness—how much light you actually see. Unlike watts, which measure energy consumption, lumens focus on the light output. This distinction is critical, especially in today’s world where energy-efficient LED and solar lighting dominate the market.
Years ago, people relied on watts to gauge brightness because traditional incandescent bulbs had a predictable relationship between energy use and light output. For example, a 60-watt bulb was brighter than a 40-watt bulb. But with modern lighting technologies like LEDs, this relationship no longer holds. A 10-watt LED can easily produce the same brightness as a 60-watt incandescent bulb, but with a fraction of the energy consumption. That’s why lumens have become the gold standard for measuring brightness—it’s the metric that tells you how much light you’re getting, regardless of the energy used.
Lumens play a pivotal role in visibility, safety, and energy efficiency. In outdoor and street lighting, the right lumen count can mean the difference between a well-lit, secure area and a dimly lit space that invites accidents or security risks. For instance, I’ve worked on projects where increasing the lumen output in parking lots and pathways significantly reduced incidents of theft and improved pedestrian safety. Bright, evenly distributed light enhances visibility, making it easier for drivers to navigate and pedestrians to feel secure.
At the same time, lumens are directly tied to energy efficiency. Over the years, I’ve helped countless clients optimize their lighting systems by balancing brightness with energy consumption. Too many lumens can lead to unnecessary energy use and light pollution, while too few can compromise safety and functionality. The key is to match the lumen output to the specific needs of the space—whether it’s a residential driveway, a commercial parking lot, or a public street.
Understanding lumens is not just about knowing how bright a light is; it’s about making informed decisions that impact safety, aesthetics, and sustainability. With the right guidance, you can achieve optimal lighting that meets your needs without wasting energy or resources.
Bulb Wattage to Lumens Comparison
| Bulb Type | Wattage (Watts) | Lumens (Brightness) |
|---|---|---|
| Incandescent | 40W | 450 lumens |
| Incandescent | 60W | 800 lumens |
| Incandescent | 75W | 1,100 lumens |
| Incandescent | 100W | 1,600 lumens |
| LED | 6-9W | 450 lumens |
| LED | 8-12W | 800 lumens |
| LED | 13-15W | 1,100 lumens |
| LED | 16-20W | 1,600 lumens |
| CFL | 9-11W | 450 lumens |
| CFL | 13-15W | 800 lumens |
| CFL | 18-20W | 1,100 lumens |
| CFL | 23-26W | 1,600 lumens |
Notes:
- Incandescent bulbs are less energy-efficient and produce fewer lumens per watt.
- LED bulbs are highly energy-efficient, producing more lumens per watt.
- CFL bulbs are more efficient than incandescent but less efficient than LEDs.
How Lumens Impact Outdoor and Street Lighting
Lumens are the cornerstone of effective outdoor and street lighting, directly influencing how well-lit and functional a space becomes. They play a critical role in various aspects:
- For Pedestrians: The right lumen count ensures clear visibility of walkways, reducing the risk of trips or falls. A well-lit path not only enhances safety but also fosters a sense of security, encouraging people to use outdoor spaces even after dark.
- For Drivers: Lumens are essential for illuminating roads, intersections, and signage. Proper lighting helps drivers react quickly to obstacles, pedestrians, or other vehicles, significantly reducing the likelihood of accidents.
- For Property Owners: Adequate lumen levels deter trespassers and enhance the overall safety of premises.
However, effective lighting isn’t just about brightness—it’s about balance. Key considerations include:
- Avoiding Glare: Excessive brightness can create glare, which is uncomfortable and hazardous, obscuring vision for both drivers and pedestrians.
- Preventing Insufficient Lighting: Too few lumens can leave areas dim and unsafe.
- Application-Specific Needs: For example:
- Residential driveways may require 1,000–2,000 lumens.
- Busy streets or parking lots may need upwards of 10,000 lumens.
Energy Efficiency
High-lumen lights don’t have to mean high energy consumption. Modern LED and solar lighting technologies provide powerful illumination with minimal energy use. By selecting fixtures with the right lumen output and energy efficiency ratings, you can achieve optimal lighting without inflating energy costs or compromising sustainability goals.
Aesthetic and Ambiance
Lumens also play a significant role in creating ambiance and enhancing aesthetics. Outdoor lighting isn’t just about functionality—it’s about setting the right mood:
- A warm, inviting glow can transform a backyard or garden into a cozy retreat.
- Crisp, bright lighting can highlight architectural features or landscaping.
- In public spaces, the right lumen levels can make parks, plazas, and streets feel welcoming and vibrant, encouraging community engagement and activity.
Ultimately, lumens are more than just a measure of brightness—they’re a tool for shaping how spaces are experienced. By understanding their impact on visibility, safety, energy efficiency, and aesthetics, you can make informed decisions that elevate both the functionality and appeal of your outdoor and street lighting projects.
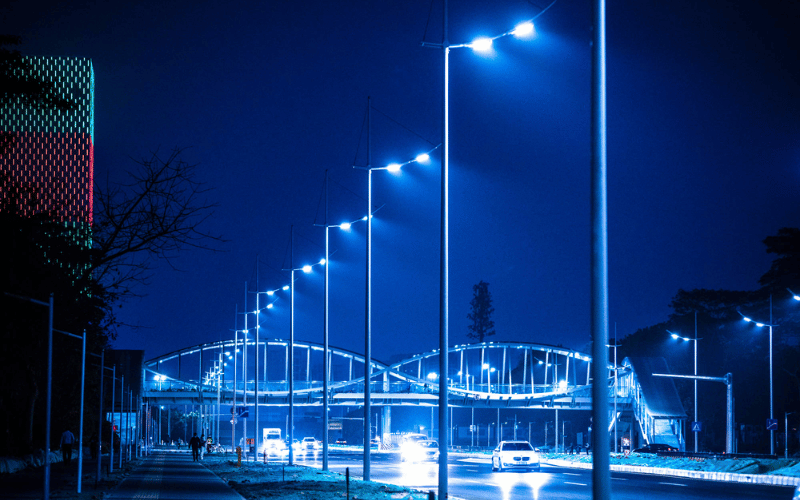

How Many Lumens Do You Need for Street Lighting?
When determining the appropriate lumens for street lighting, it’s essential to approach the decision with precision and a clear understanding of the variables at play. Proper lighting not only ensures safety and visibility but also optimizes energy efficiency and compliance with local standards. Below, I’ll break down the key factors to consider and provide actionable guidelines to help you make informed decisions.
Factors to Consider
-
Road Type
The type of road being illuminated significantly impacts the required lumen output. Residential streets, for instance, demand less intense lighting compared to highways, where higher speeds and heavier traffic necessitate brighter illumination for safety. -
Pole Height and Spacing
The height of the poles and the distance between them directly influence the light distribution and intensity. Taller poles require higher lumen outputs to ensure adequate ground coverage, while closer spacing can reduce the need for extremely high lumens per fixture. -
Traffic Volume and Speed
Roads with higher traffic volumes or faster-moving vehicles require brighter lighting to enhance visibility and reduce the risk of accidents. For example, a quiet residential street won’t need the same level of brightness as a busy urban thoroughfare. -
Local Regulations and Lighting Standards
Many municipalities and regions have specific lighting standards that dictate minimum lumen levels, uniformity ratios, and color temperature. Always consult these regulations to ensure compliance and avoid costly retrofits.
General Guidelines for Lumen Requirements
To simplify the decision-making process, here are some general recommendations based on road type, pole height, and typical use cases:
| Road Type | Pole Height | Recommended Lumens | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small lanes | ~4 meters | ~2,000 lumens | Ideal for narrow residential streets or pathways with low traffic. |
| Moderate roads | ~6 meters | ~4,000 lumens | Suitable for suburban streets or secondary roads with moderate traffic. |
| Busy roads | ~8 meters | 8,000–10,000 lumens | Designed for urban roads with significant traffic and higher speeds. |
| Highways | Over 8 meters | Based on local regulations | Consult standards for highways, as requirements vary by region and usage. |
Expert Insights
When planning street lighting, it’s crucial to balance brightness with energy efficiency. Over-lighting can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and light pollution, while under-lighting compromises safety. For instance, on a residential street with minimal traffic, a 2,000-lumen fixture on a 4-meter pole provides sufficient illumination without being intrusive. Conversely, a busy urban road with 8-meter poles benefits from fixtures delivering 8,000 lumens or more to ensure clear visibility for drivers and pedestrians alike.
Additionally, consider the beam angle and light distribution pattern of your fixtures. A well-designed luminaire with precise optics can reduce the number of fixtures needed, cutting costs without sacrificing performance. Always conduct a lighting simulation or photometric analysis to validate your design before installation.
By carefully evaluating these factors and adhering to the guidelines above, you can achieve a lighting solution that is both effective and efficient, ensuring safety and compliance for years to come.
How Many Lumens Do You Need?
When determining the appropriate lumens for your solar street lighting project, it’s essential to consider the specific application and environment. Lumens measure the total visible light emitted by a source, and selecting the right level ensures optimal functionality, safety, and aesthetics. Below, I’ll break down recommendations for both residential and commercial applications, along with key factors to guide your decision-making process.
Residential Lighting Recommendations:
- Pathways and Walkways (100-200 lumens): For pathways and walkways, the goal is to provide enough light to ensure safe navigation without overwhelming the surroundings. A soft, diffused light in this range is ideal for creating a welcoming ambiance while avoiding glare. Consider fixtures with a wide beam angle to evenly illuminate the path.
- Driveways (1,000-2,000 lumens): Driveways require brighter lighting to enhance visibility for vehicles and pedestrians. This range ensures clear sightlines, especially in areas with limited ambient light. Opt for fixtures with focused beams to direct light where it’s needed most, minimizing light spill.
- Backyards and Patios (500-1,500 lumens): The lighting here should balance functionality and comfort. Lower lumens work well for creating a cozy atmosphere, while higher lumens are better for task-oriented spaces like outdoor kitchens or seating areas. Adjustable fixtures can help you tailor the lighting to different activities.
- Security Lighting (1,500-3,000 lumens): Security lighting demands higher brightness to deter intruders and improve visibility around entry points. Motion-activated lights in this range are particularly effective, as they conserve energy while providing a strong deterrent when triggered.
Commercial and Public Lighting Needs:
- Parking Lots (10,000-20,000 lumens): Parking lots require high-intensity lighting to ensure safety for both drivers and pedestrians. Uniform light distribution is critical to eliminate dark spots and reduce the risk of accidents. Fixtures mounted at higher poles (20-30 feet) often fall within this lumen range.
- Street Lighting (15,000-30,000 lumens): For roadways, the focus is on providing consistent, bright lighting to enhance visibility for drivers and pedestrians. The exact lumen requirement depends on the width of the road, traffic volume, and surrounding ambient light. High-efficiency LED fixtures with precise optics are recommended to minimize light pollution.
- Parks and Public Spaces (3,000-6,000 lumens): Parks and recreational areas benefit from softer, evenly distributed lighting that enhances safety without disrupting the natural environment. Lower lumens are suitable for pathways, while higher lumens may be needed for open spaces or activity zones.
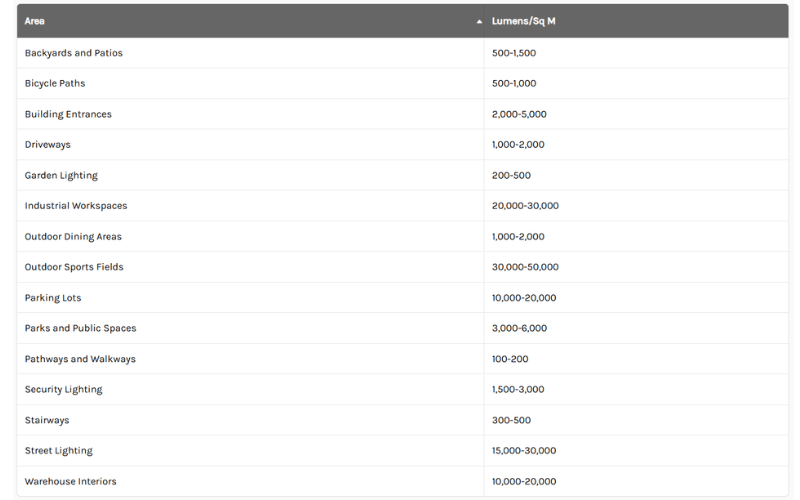
Lumens Requirements for Common Areas
| Area | Lumens/Sq M |
|---|---|
| Pathways and Walkways | 100-200 |
| Driveways | 1,000-2,000 |
| Backyards and Patios | 500-1,500 |
| Security Lighting | 1,500-3,000 |
| Parking Lots | 10,000-20,000 |
| Street Lighting | 15,000-30,000 |
| Parks and Public Spaces | 3,000-6,000 |
| Outdoor Sports Fields | 30,000-50,000 |
| Building Entrances | 2,000-5,000 |
| Stairways | 300-500 |
| Bicycle Paths | 500-1,000 |
| Outdoor Dining Areas | 1,000-2,000 |
| Garden Lighting | 200-500 |
| Warehouse Interiors | 10,000-20,000 |
| Industrial Workspaces | 20,000-30,000 |
Factors to Consider When Choosing Lumens:
- Purpose of the Lighting: Define whether the primary goal is safety, aesthetics, or a combination of both. For example, security lighting prioritizes brightness and coverage, while decorative lighting focuses on ambiance.
- Size of the Area and Mounting Height: Larger areas and higher mounting poles require more lumens to achieve adequate illumination. For instance, a 20-foot pole in a parking lot will need a higher lumen output than a 10-foot pole in a backyard.
- Light Distribution and Beam Angle: The beam angle determines how light is spread across an area. Narrow beams concentrate light on specific spots, while wider beams provide broader coverage. Choose fixtures with optics designed for your application to maximize efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency Goals: Solar-powered and LED lighting options are highly efficient, offering significant energy savings over traditional lighting. LEDs provide higher lumens per watt, allowing you to achieve the desired brightness with lower energy consumption. Pairing LEDs with solar panels ensures sustainable, off-grid operation.
By carefully evaluating these factors and aligning them with your specific needs, you can select the right lumen output to achieve optimal performance and efficiency for your lighting project.
Application-Specific Lumen Recommendations
Security Lighting
When it comes to security lighting, precision is key. Focused lighting with narrow beam angles, typically in the range of 300-700 lumens, ensures that the light is directed exactly where it’s needed without unnecessary spillover. This not only enhances security but also minimizes light pollution. For instance, a 500-lumen spotlight with a 30-degree beam angle positioned above a garage door can effectively illuminate the driveway and deter intruders. Similarly, a 700-lumen motion-activated floodlight placed at the back of a property can cover entry points like doors or windows without overwhelming the surrounding area. The goal is to create a sense of safety while maintaining a balance between functionality and subtlety.
Tree Lighting
Tree lighting is an art form that combines technical precision with aesthetic sensibility. The lumen range you choose should correspond to the height and density of the tree. For smaller trees, 500-800 lumens are sufficient to highlight their structure and foliage. For taller or more expansive trees, 1,000-1,500 lumens may be necessary to achieve the desired effect. To create a dramatic yet understated look, consider using uplights with adjustable beam angles. For example, a 700-lumen spotlight with a 15-degree beam can accentuate the trunk, while a 1,200-lumen fixture with a wider beam can softly illuminate the canopy. Layering light in this way adds depth and dimension, transforming trees into focal points without overpowering the landscape.
Wall-Mounted Lamps
Wall-mounted lamps serve both decorative and functional purposes, and a lumen range of 300-500 is ideal for achieving this balance. At 300 lumens, you can create a warm, inviting glow for entryways or patios, while 500 lumens provide enough brightness for tasks like unlocking doors or navigating pathways. To avoid glare, opt for fixtures with frosted glass or downward-facing designs. For example, a 400-lumen sconce with a shielded bulb can cast a soft, diffused light that enhances the architectural features of your home without disturbing neighbors. Thoughtful placement and design ensure that your lighting is both effective and considerate.
Post Top Lights
Post top lights are often used to mark gates, driveways, or property boundaries, and a lumen range of 500-700 is typically sufficient. The key is to strike a balance between security and style. For instance, a 600-lumen fixture with a classic lantern design can provide ample illumination for a gate while adding a touch of elegance. To enhance visibility without creating harsh contrasts, consider using fixtures with diffusers or frosted panels. This approach ensures that the light is evenly distributed, creating a welcoming atmosphere that also serves a practical purpose.
Garden Pole Lights
Garden pole lights are versatile fixtures that can enhance both ambiance and safety. The appropriate lumen range depends on the height of the pole. For shorter poles (2-3 feet), 500-700 lumens are ideal for softly illuminating pathways or flower beds. For taller poles (4-6 feet), 800-1,000 lumens can provide broader coverage for larger garden areas. To create a cohesive look, use warm white light (around 3,000K) and position the poles at regular intervals along pathways or around seating areas. For example, a series of 700-lumen garden poles spaced 10 feet apart can guide visitors through a garden while highlighting its features in a subtle, inviting way.
Street Lighting
Street lighting requires careful consideration of pole height and road type to ensure safety and visibility. For residential streets with poles around 10-15 feet high, 2,000-4,000 lumens are typically sufficient. For main roads or highways with taller poles (20-30 feet), lumen levels can range from 6,000 to 10,000 or more. Uniform light distribution is critical to avoid dark spots and ensure consistent visibility for drivers and pedestrians. For example, a 4,000-lumen LED fixture with a Type II distribution pattern can effectively light a residential street, while a 10,000-lumen fixture with a Type III or Type IV pattern is better suited for wider roads or intersections. Proper spacing and alignment of fixtures further enhance safety and reduce glare, creating a well-lit environment that feels secure and welcoming.

The Role of LED and Solar Lighting in Lumen Efficiency
LED and solar lighting technologies have revolutionized the way we think about lumen efficiency, offering a combination of high performance and sustainability that traditional lighting simply cannot match. At the core of this transformation is the ability of LEDs to convert energy into light with remarkable precision. Unlike conventional bulbs, which lose a significant portion of energy as heat, LEDs are designed to maximize lumen output while consuming minimal power. For example, a 30-watt LED streetlight can produce the same brightness as a 100-watt high-pressure sodium (HPS) lamp, reducing energy consumption by up to 70%.
When paired with solar technology, the efficiency gains become even more compelling. Solar panels harness sunlight during the day, storing energy in batteries to power LEDs at night. This closed-loop system eliminates the need for grid electricity, making it an ideal solution for remote or off-grid locations. Advanced solar controllers further optimize energy use by adjusting light output based on real-time conditions, such as dimming during low-traffic hours to conserve power without compromising safety.
Comparing LED Streetlights to Traditional Lighting
The advantages of LED streetlights over traditional lighting systems extend beyond energy efficiency. Durability is a key factor. LEDs have a lifespan of 50,000 to 100,000 hours, compared to the 10,000-20,000 hours typical of HPS or metal halide lamps. This means fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs over time. Additionally, LEDs are more robust, withstanding extreme temperatures and vibrations that can easily damage traditional bulbs.
From a cost perspective, the initial investment in LED and solar lighting may be higher, but the long-term savings are undeniable. Reduced energy consumption, minimal maintenance, and the elimination of electricity bills for solar-powered systems result in a significantly lower total cost of ownership. For instance, a municipality that replaces 1,000 HPS streetlights with LED solar lights could save tens of thousands of dollars annually in energy and maintenance costs.
Environmental Benefits of Energy-Efficient Lighting
The environmental impact of switching to LED and solar lighting is profound. By consuming less energy, these systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation. Solar-powered LEDs take this a step further by relying entirely on renewable energy, eliminating carbon emissions altogether. Additionally, LEDs contain no hazardous materials like mercury, which is commonly found in traditional bulbs, making them safer to manufacture, use, and dispose of.
Another often-overlooked benefit is the reduction of light pollution. LEDs can be precisely directed to illuminate specific areas, minimizing spillover and preserving the natural night sky. This is particularly important in urban areas where excessive lighting can disrupt ecosystems and human circadian rhythms.
In summary, LED and solar lighting technologies are not just about brighter streets—they represent a smarter, more sustainable approach to illumination. By maximizing lumen efficiency, reducing costs, and protecting the environment, they set a new standard for what lighting can achieve.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Lumens
Selecting the right lumens for a lighting project is not just about brightness—it’s about achieving the perfect balance of functionality, efficiency, and aesthetics. Missteps in this process can lead to significant issues, from safety hazards to wasted resources. Here are the most common mistakes I’ve seen and how to avoid them.
Over-Lighting: The Hidden Costs of Too Much Light
One of the most frequent errors is over-lighting, where fixtures emit far more lumens than necessary. While it might seem like more light equals better visibility, the reality is quite different. Excessive brightness can create glare, which reduces visibility rather than enhancing it. For example, a 3,000-lumen floodlight aimed at a driveway might blind drivers or pedestrians, making it harder to see hazards.
Over-lighting also contributes to light pollution, which disrupts ecosystems, obscures the night sky, and negatively impacts human health by interfering with sleep patterns. Beyond these environmental and social concerns, over-lighting wastes energy, driving up costs unnecessarily. A better approach is to assess the specific needs of the area being lit. For instance, a residential pathway might only require 300-500 lumens, while a parking lot could need 2,000-4,000 lumens, depending on its size and usage.
Under-Lighting: Compromising Safety and Functionality
On the flip side, under-lighting is equally problematic. Insufficient lumens can leave critical areas poorly illuminated, compromising safety and functionality. For example, a streetlight with only 1,000 lumens on a busy roadway will fail to provide adequate visibility for drivers and pedestrians, increasing the risk of accidents. Similarly, a garden path lit with dim fixtures might look charming but could become a tripping hazard.
To avoid under-lighting, it’s essential to consider the purpose of the lighting and the environment it will serve. A good rule of thumb is to match lumen output to the task at hand. For instance, security lighting around entry points should deliver focused brightness (300-700 lumens) to deter intruders, while decorative garden lighting can use lower lumens (200-400) to create ambiance without sacrificing safety.
Ignoring Beam Angles and Light Distribution: The Role of Fixture Design
Another common oversight is neglecting the importance of beam angles and light distribution. Lumens alone don’t determine how well an area is lit; the design of the fixture plays a critical role. A poorly designed fixture with a wide beam angle might scatter light inefficiently, leaving key areas in shadow while wasting light on unnecessary spaces. For example, a 1,000-lumen fixture with a 120-degree beam angle might spread light too thinly over a large area, whereas a 60-degree beam angle would concentrate the light where it’s needed most.
When choosing fixtures, consider the specific application. For street lighting, look for fixtures with Type II or Type III light distribution patterns to ensure even coverage along roadways. For security lighting, narrow beam angles (15-30 degrees) are ideal for focusing light on entry points or specific zones. Properly designed fixtures not only enhance functionality but also reduce energy consumption by directing light precisely where it’s needed.
Avoiding these common mistakes requires a thoughtful approach to lumen selection, one that considers not just brightness but also the broader context of the lighting environment. By addressing over-lighting, under-lighting, and fixture design, you can create lighting solutions that are efficient, effective, and tailored to the needs of the space.
FAQs
Q: What is a lumen?
A: A lumen measures the amount of visible light emitted by a source. It indicates the brightness of a light fixture, helping you understand how much light it will produce. Unlike watts, which measure energy consumption, lumens focus solely on light output.
Q: How many lumens do I need for outdoor security lighting?
A: For outdoor security lighting, you typically need 300-700 lumens. This range provides enough brightness to illuminate entry points, driveways, or pathways without causing glare or wasting energy. Choose fixtures with focused beam angles to direct light where it’s needed most.
Q: What’s the difference between lumens and watts?
A: Lumens measure light output, while watts measure energy consumption. In the past, people used watts to estimate brightness because traditional bulbs had a predictable watt-to-brightness ratio. With energy-efficient LEDs, lumens now provide a more accurate way to gauge brightness, as LEDs use far fewer watts to produce the same amount of light.
Q: Can high-lumen lights improve road safety?
A: High-lumen lights can improve road safety by enhancing visibility for drivers and pedestrians. However, brightness alone isn’t enough. Proper light distribution, beam angles, and uniformity play critical roles in reducing glare and ensuring consistent illumination across roadways.
Q: Are LED lights better for outdoor and street lighting?
A: Yes, LED lights are better for outdoor and street lighting. They offer superior energy efficiency, longer lifespans, and better lumen output compared to traditional lighting. LEDs also provide precise light control, reducing glare and light pollution while ensuring even illumination for safety and aesthetics.
Conclusion
Understanding lumens is essential for creating effective lighting solutions. By tailoring lumen output to specific applications—whether it’s security, tree lighting, or street illumination—you can achieve the perfect balance of functionality and aesthetics. Energy-efficient technologies like LEDs and solar lighting further enhance this process, delivering maximum brightness with minimal energy use. Take the time to assess your unique needs, from beam angles to light distribution, and make informed choices that prioritize safety, elevate aesthetics, and promote sustainability.